SUSTAINABILITY
Environment, Social and Governance (ESG)
GLOBAL GOALS & CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
Member of the following Sustainability Associations

Incorporating Sustainable Business Practices Is a Key Area of Focus for Organizations
Companies are seeing a consistent increase in pressure from investors, employees, customers, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and numerous other stakeholders to increase transparency on sustainable and socially responsible practices, articulated through Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting.
Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) are the three central pillars in the measurement of sustainability and societal impact of an investment and are deemed to be the criteria to determine the future financial performance of companies.
- Environment criteria consider a company’s use of resources and stewardship of nature.
- Social criteria examine a company’s commercial relationship with employees, customers, communities, and other key stakeholders.
- Governance encompass accurate and transparent methods of accounting, the company’s leadership, internal controls and audits, and shareholder rights.
Ensuring you have a strong ESG proposition creates higher value for your company. This can be seen through top-line growth, cost reductions, regulatory and legal interventions, optimization of assets, and improved productivity. Employee productivity will improve with a strong ESG proposition as well as enhancing employee motivation and attracting quality employees. An employee’s interest in their work is motivated by their perception of impact on the beneficiaries of their work.
When it comes to ESG, companies need to be ready to play a long game. To maximize the value they need to work at satisfying the needs of their customers, employees, and surrounding communities. Investors today are requesting transparency across the board regarding how companies are addressing environmental, social, and governance criteria which means companies are being made accountable for their actions which creates value.

Alignment of UNSDGs and ESG
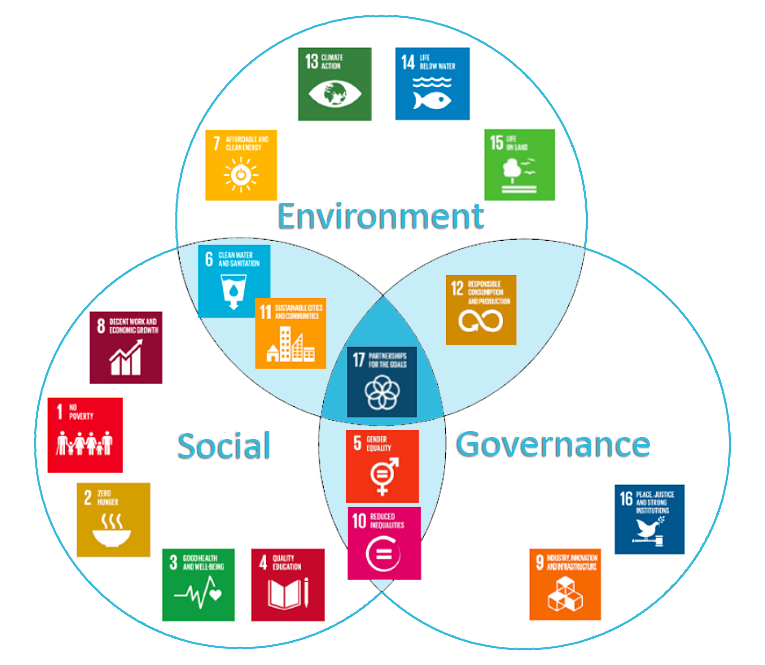
The UNSDGs Can Help Develop Your ESG Plan
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are increasingly being recognized as a beneficial foundation for responsible investment as the world shifts its focus more intently on ESG (Environment, Social, Governance). As of February 2018, over 40% of the G250, the world’s 250 largest firms, acknowledge the SDGs in their corporate reporting and include the global goals in their CEO and/or Chair’s statement, according to Harvard Law.
To meet increasing stakeholder demand, some businesses are moving beyond the standard ESG approach, which measures performance by limiting corporate impact, and instead of searching for ways to improve the world around them and have a positive, measurable influence. In turn, the SDGs offer a realistic framework for ESG mapping at a higher level and can help to increase the adoption of sustainable investing, encourage responsible corporate behavior, and integrate sector and business specific ESG factors with broader social issues and global environmental goals.
How the SDGs support ESG planning & outcomes
The SDGs were established to achieve a worldwide consensus on serious and widespread social and environmental issues. Because the SDGs are internationally recognized, they impact all countries and sectors on a macroeconomic level, meaning investors and businesses can utilize them to assess the impact of ESG investment strategies and set ESG goals.
A strengthened framework
Scenarios based on the SDGs can give ESG issues a new perspective. By connecting SDGs to current ESG measures, companies and investors can establish a common vocabulary for business decision-making and investment strategies. Furthermore, the SDGs allow businesses to consider financially significant regulatory, operational, and ethical problems related to the goals, which strengthens their existing ESG frameworks.
Ready to start a conversation about achieving breakthrough results?



